Achilles Tendinitis Treatment
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
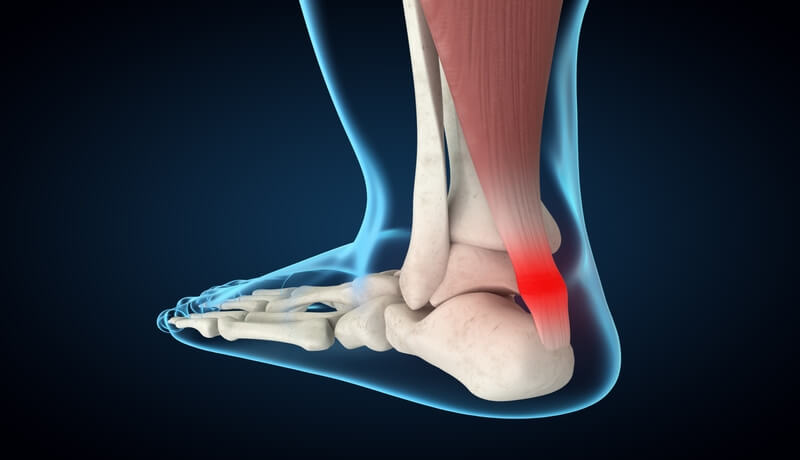
What is achilles tendinitis?
Achilles tendinitis is when the Achilles tendon, which connects your calf muscles to your heel, gets irritated or inflamed. This usually happens because of overuse, like running too much or doing sports without warming up properly. It can cause pain and stiffness in the back of your leg, especially after resting or in the morning. Most cases can be treated at home with rest, ice, and exercises, but if it gets worse, it might tear and need surgery. If you feel pain in your Achilles tendon, it’s important to rest and see a doctor if it doesn’t get better.
Achilles tendinitis is a condition that results from repetitive stress or overuse of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone (calcaneus). This tendon plays a crucial role in walking, running, and jumping, making it susceptible to injury if overworked. Achilles tendinitis primarily occurs due to increased physical activity, such as running or sports that involve sudden starts and stops, like tennis or basketball. It is particularly common among athletes and middle-aged individuals who engage in physical activities during weekends without regular conditioning.
What is Achilles Tendinitis?
The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body, allowing you to point your toes and push off when walking or running. Achilles tendinitis refers to inflammation, irritation, or micro-tears in the tendon resulting from repetitive strain. While mild cases may involve discomfort during activity, severe tendinitis can lead to intense pain and affect everyday movements. In some cases, if left untreated, the condition may progress to an Achilles tendon rupture, which requires immediate medical attention and possibly surgery.
Causes of Achilles Tendinitis
A common cause of Achilles tendinitis is overuse. Activities that put excessive strain on the tendon, such as running longer distances or increasing the intensity of exercise without proper preparation, often lead to inflammation. Other contributing factors include:
- Sudden Increase in Physical Activity: A rapid increase in training intensity or duration can put excess strain on the Achilles tendon.
- Tight Calf Muscles: Lack of flexibility in the calf muscles can increase tension on the tendon, making it more prone to injury.
- Poor Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide adequate support or cushioning can exacerbate stress on the Achilles tendon.
- Improper Training Techniques: Not warming up properly, poor running form, or overtraining can increase the risk of Achilles tendinitis.
- Age: As we age, the Achilles tendon can weaken, increasing the risk of tendinitis, particularly in middle-aged individuals.
Symptoms of Achilles Tendinitis
Symptoms of Achilles tendinitis can vary in intensity, but typically include:
- Discomfort or Stiffness: A dull ache or stiffness in the back of the leg, usually just above the heel, especially after prolonged rest or in the morning.
- Tenderness: The affected area may feel tender to the touch, and swelling may occur along the tendon.
- Pain During Activity: Pain may become more noticeable during activities like running, climbing stairs, or jumping.
- Limited Range of Motion: Stiffness and pain may limit the ability to flex the foot, resulting in reduced range of motion.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent pain or discomfort in the Achilles tendon that does not improve with rest, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Immediate medical attention is necessary if:
- You experience sudden, severe pain in the back of your leg or near your heel.
- You are unable to walk properly due to pain or weakness in your calf or foot.
- You hear a popping sound or feel as though you were kicked in the back of the leg, which may indicate a tendon rupture.
Diagnosis of Achilles Tendinitis
To diagnose Achilles tendinitis, your doctor will review your symptoms and medical history, followed by a physical examination. Imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI may be recommended to assess the severity of tendon damage and rule out other conditions, such as a rupture.
Treatment Options for Achilles Tendinitis
Most cases of Achilles tendinitis can be treated with non-surgical methods. These treatments aim to reduce inflammation and promote healing while preventing further injury. Common treatment approaches include:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the pain. Resting the affected leg allows the tendon to heal.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the painful area several times a day can help reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Compression and Elevation: Wrapping the leg or wearing a compression sleeve and keeping the leg elevated can reduce swelling.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Physical therapy exercises that stretch and strengthen the calf muscles can help alleviate tension on the Achilles tendon.
- Orthotic Devices: Shoe inserts or heel lifts may be recommended to reduce strain on the tendon.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen can help manage pain and reduce inflammation.
In severe cases or when conservative treatments are not effective, your doctor may recommend:
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections: This treatment involves injecting concentrated platelets from your own blood into the damaged tendon to promote healing.
- Surgery: If the Achilles tendon has torn, surgery may be required to repair the tendon and restore normal function. Surgery may also be recommended for chronic tendinitis that does not respond to other treatments.
Preventing Achilles Tendinitis
To prevent Achilles tendinitis or reduce the risk of recurrence, consider the following strategies:
- Gradually Increase Activity Levels: When starting a new exercise routine or increasing your workout intensity, make gradual changes to give your body time to adapt.
- Warm-Up Properly: Always start your exercise session with a proper warm-up, including dynamic stretches for your calf muscles.
- Wear Appropriate Footwear: Choose shoes that provide good arch support and cushioning, particularly during high-impact activities.
- Strengthen Calf Muscles: Regular strengthening exercises for your calf muscles can help improve tendon resilience.
- Stretch Regularly: Stretching your calves and Achilles tendons can enhance flexibility and reduce strain.
Conclusion
Achilles tendinitis is a common injury that can significantly impact daily activities and athletic performance if left untreated. However, with early intervention and appropriate care, most cases can be successfully managed at home with rest, ice, and physical therapy. In more severe cases, medical treatments or even surgery may be required. To prevent recurrence, it’s important to practice proper warm-up techniques, wear supportive footwear, and maintain good flexibility and strength in the lower leg muscles.
Always consult your healthcare provider if you experience persistent pain or discomfort around the Achilles tendon, as early diagnosis and treatment can prevent more serious complications.
Request your Appointment by clicking on the picture below.