Underactive thyroid symptoms
Overview
Hypothyroidism, commonly referred to as underactive thyroid disease, occurs when your thyroid gland fails to produce and release enough hormones into your bloodstream. As a result, the condition slows down your metabolism, which can lead to unexpected weight gain and persistent fatigue. Fortunately, hormone replacement therapy is the most common and effective treatment for managing an underactive thyroid.

What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition that arises when your thyroid gland does not produce sufficient amounts of hormones. The thyroid gland is crucial for regulating metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and overall energy levels. Consequently, when hormone production is inadequate, your metabolism slows, which may result in unintended weight gain and a constant feeling of exhaustion.
While weight gain and fatigue are common symptoms, they are not specific to hypothyroidism. Therefore, a simple blood test can assist your healthcare provider in confirming this condition. In general, hypothyroidism is highly treatable, and most people can effectively manage the condition through medication and regular follow-up visits with their endocrinologist.
However, if left untreated over extended periods, hypothyroidism can lead to severe health complications, potentially becoming life-threatening. Thus, if you notice new symptoms, it’s vital to seek evaluation and treatment.
Types of Hypothyroidism
There are four primary types of hypothyroidism:
- Primary Hypothyroidism: This type directly impacts the thyroid, leading to low levels of thyroid hormones. Consequently, your pituitary gland produces more thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in response. Autoimmune conditions such as Hashimoto’s disease often cause this type, along with thyroid surgery or radiation therapy. Notably, primary hypothyroidism is the most common type.
- Secondary Hypothyroidism: This occurs due to an underactive pituitary gland, which fails to send adequate TSH signals to the thyroid. Secondary hypothyroidism is quite rare.
- Tertiary Hypothyroidism: This happens when the hypothalamus does not produce enough thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), leading to insufficient TSH production by the pituitary gland.
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism: Also known as mild thyroid failure, this type involves slightly elevated TSH levels while all other thyroid hormone levels remain within a typical range. Fortunately, subclinical hypothyroidism often resolves on its own within about three months.
How Common is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism can affect anyone; however, it is most prevalent among individuals assigned female at birth (AFAB) who are over 60, especially post-menopause. Furthermore, family history and certain medical conditions can also influence its occurrence.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the Symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
Symptoms of hypothyroidism typically develop slowly over time and may take years to manifest fully. Some common symptoms include:
- Brain fog, including forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating
- Depression and anxiety
- Dry, coarse skin and hair
- Elevated blood cholesterol levels
- Persistent fatigue
- Frequent or heavy menstrual periods
- Hoarseness
- Inability to tolerate cold temperatures
- Numbness or tingling in your hands
- Physical changes in your face, such as drooping eyelids and puffiness around your eyes
- Soreness or muscle weakness
- Unexplained weight gain
If you develop any signs of hypothyroidism, inform your healthcare provider. They can run tests to confirm a diagnosis.
What Causes Hypothyroidism?
The most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. However, other causes include:
- Certain medications, such as lithium, thalidomide, and amiodarone
- Congenital conditions, such as being born without a functioning thyroid gland
- Iodine deficiency, resulting from inadequate iodine in the body
- Pituitary gland disorders, including noncancerous tumors
- Thyroiditis, which is inflammation of the thyroid that can occur after a viral illness or during pregnancy
What are the Risk Factors for Hypothyroidism?
Although anyone can develop hypothyroidism, certain factors increase your risk. These include:
- Being assigned female at birth (AFAB)
- Having an autoimmune disease
- Genetic predisposition, such as a biological parent or sibling with the condition
- A history of thyroid surgery, including thyroid gland removal
- Pregnancy
- Previous history of head and neck radiation therapy
- Starting or stopping certain medications
Complications of Hypothyroidism
With effective treatment, complications from hypothyroidism are rare. However, if left untreated, the condition can lead to serious health issues, such as:
- Goiter, an enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Heart problems, including an increased risk of heart disease
- Infertility or complications during pregnancy
- Miscarriage or birth defects
- Pituitary neuropathy, which can lead to nerve damage
- Myxedema coma, a rare and life-threatening complication that affects multiple organs
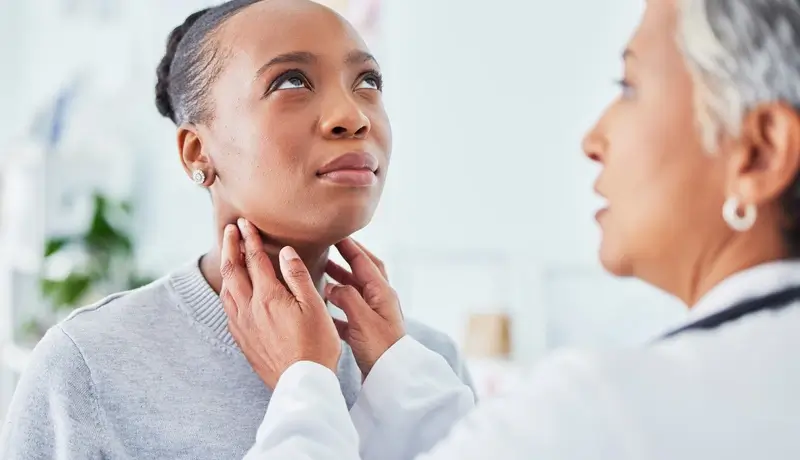

Diagnosis and Tests
How is Hypothyroidism Diagnosed?
A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination, pressing gently around your thyroid to check for swelling. They will also inquire about your symptoms and review your medical history thoroughly.
To accurately diagnose hypothyroidism, healthcare providers typically conduct thyroid tests. This is important because an underactive thyroid can exhibit symptoms similar to those of other unrelated health conditions. Blood tests will measure the levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), as well as the levels of the thyroid hormones (T3 and T4).
You may also need imaging tests of your thyroid, which could include:
- Ultrasound
- CT (computed tomography) scan
- Thyroid uptake scan, a type of nuclear medicine imaging
Management and Treatment
How is Hypothyroidism Treated?
The most common treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement therapy. The medication levothyroxine (Synthroid®, Levo-T®) replaces the hormones that your thyroid cannot produce naturally. Most people take it in the mornings on an empty stomach, and when taken daily, levothyroxine can stabilize hormone levels and alleviate symptoms.
Finding the right dosage often involves some trial and error; therefore, your provider will conduct routine blood tests until your TSH levels normalize. It is crucial to note that you will need to take hypothyroidism medication for life. With careful management and regular follow-ups with your healthcare provider, you can maintain a normal and healthy life.
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better?
Levothyroxine works quickly to level out your hormones; however, it may take a few weeks before you notice improvements in your symptoms. Be mindful that discontinuing your medication can lead to a return of symptoms.
Prevention
Can Hypothyroidism be Prevented?
Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent hypothyroidism. However, if you develop symptoms like those mentioned above, it is vital to inform your healthcare provider immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment can reduce your risk of complications and support a healthy lifestyle.

Outlook / Prognosis
Can Hypothyroidism be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for hypothyroidism. However, with effective hormone replacement therapy, you can manage the condition successfully.
How Long Does Hypothyroidism Last?
Hypothyroidism is a chronic condition that requires lifelong management. If you receive a diagnosis, you will need to take medication every day to maintain balanced thyroid hormone levels.
Outlook for Hypothyroidism
With proper treatment, individuals with hypothyroidism can expect a favorable outlook. Conversely, if left untreated, an underactive thyroid may lead to severe and life-threatening complications, such as myxedema.
Living With Hypothyroidism
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider?
If you experience symptoms like weight gain, dry skin,
or fatigue, it is important to notify your healthcare provider. They may conduct tests to rule out other potential conditions and confirm a diagnosis of hypothyroidism. Additionally, if you are already on medication for hypothyroidism and notice that your symptoms return or persist, inform your provider as they may need to adjust your dosage.
When Should I Go to the ER?
You should call 911 or go to your nearest emergency room if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Difficulty breathing: This may indicate severe complications related to hypothyroidism.
- Extreme lethargy: An overwhelming sense of fatigue that prevents you from functioning may signal a serious issue.
- Low body temperature (hypothermia): A dangerously low body temperature can be life-threatening.
- Low blood pressure (hypotension): Significantly low blood pressure can lead to shock.
- Slow heartbeat (bradycardia): A significantly slowed heart rate can pose serious health risks.
These symptoms may indicate myxedema, a life-threatening condition associated with untreated hypothyroidism. Immediate treatment is essential.
If you are experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, brain fog, depression, or unexplained weight gain, it is essential to recognize that these could be warning signs of hypothyroidism. While it can be concerning, it is important to understand that hypothyroidism can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. If you notice any troubling symptoms, do not hesitate to contact your healthcare provider for an evaluation. They can perform the necessary tests to confirm a diagnosis and recommend suitable treatment to help you regain your health and well-being.
Additional Common Questions
1. Can I Get Hypothyroidism During Pregnancy?
- Individuals with an underactive thyroid (especially primary hypothyroidism) are at an increased risk for infertility and pregnancy-related complications such as gestational hypertension and postpartum hemorrhage. Regular thyroid function tests and medication adjustments can help ensure a healthy pregnancy. If you have hypothyroidism and believe you might be pregnant, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate management strategies.
2. What Should I Know About Hypothyroidism in Children?
- Some individuals are born with an underactive thyroid or no thyroid gland at all, a condition known as congenital hypothyroidism. Healthcare providers routinely test all newborns for hypothyroidism, as adequate thyroid hormone levels are essential for an infant’s growth and brain development. If congenital hypothyroidism is detected, treatment typically begins within the first weeks of life to prevent intellectual disabilities and developmental delays.
3. Is Hypothyroidism Genetic?
- Hypothyroidism can have a genetic component, but it is not exclusively hereditary. Parents may pass the condition down to their biological children, but environmental factors, such as thyroiditis or iodine deficiency, may also play a significant role in its development.
4. Can Hypothyroidism Cause Anxiety?
- Yes, hypothyroidism can contribute to anxiety and depression. Any dysfunction of the thyroid gland can have significant effects on mental health, but hypothyroidism is particularly linked to these symptoms. Consult your healthcare provider about strategies to manage stress and promote mental well-being.
Request your Appointment by clicking on the picture below.