Prostate Cancer Detection and Treatment
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a major health concern, especially among men in the United States. It ranks as one of the most common types of cancer. The disease can develop in various ways. Some forms grow slowly, while others spread more rapidly. Due to this variation, early detection and tailored treatment are crucial. These can dramatically improve outcomes, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing the chances of successful management.
What is Prostate Cancer?
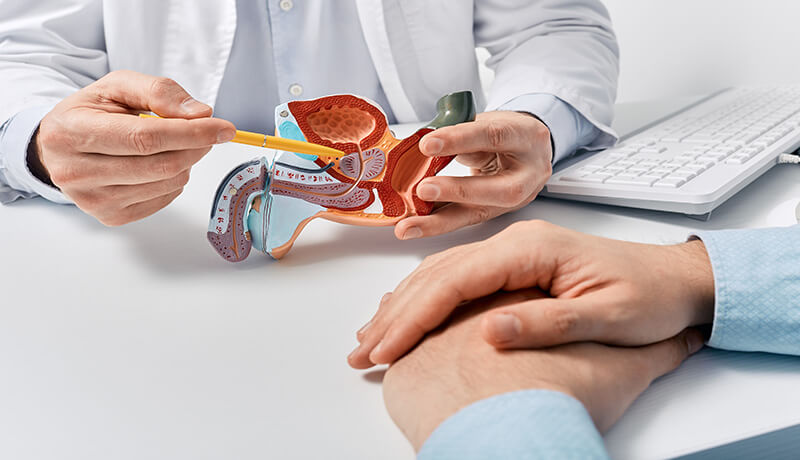
The prostate plays a crucial role in the male reproductive system. This small gland, about the size of a walnut, is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder out through the penis. The prostate produces a thick, white fluid. This fluid mixes with sperm from the testicles to form semen. The fluid is essential for sperm mobility, making it a critical factor in male fertility. Any changes in the prostate, such as those caused by cancer, can significantly affect urinary function and reproductive health.
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Understanding the risk factors associated with prostate cancer is essential for early detection and prevention. While any man can develop prostate cancer, certain factors increase the likelihood of its occurrence. Being aware of these risks can help men take proactive steps to monitor their health and seek medical advice when necessary.
- Age: Prostate cancer becomes more likely as men age. Most cases occur in men over 50. Regular screenings become increasingly important with age.
- Racial and Ethnic Background: Black men are at higher risk of developing prostate cancer compared to other racial groups. Additionally, they often face more aggressive forms of the disease.
- Family History: A family history of prostate cancer significantly raises the risk. Men with a father or brother who had prostate cancer are more likely to develop it, especially if their relatives were diagnosed at a young age.
- Genetic Markers: Certain genetic mutations, such as those in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, increase the risk. These genes are also linked to higher risks of breast and ovarian cancers in women. Men carrying these markers should discuss their risks with a healthcare provider and consider more frequent screenings.
Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and better outcomes. Regular screening is recommended, especially for men with higher risk factors. Several diagnostic tools help detect prostate cancer in its early stages. Understanding these methods allows men to make informed decisions about their health.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
The PSA test measures the level of prostate-specific antigen in the blood. PSA is a protein produced by both cancerous and noncancerous tissue in the prostate. Elevated levels may indicate the presence of cancer. However, other conditions like an enlarged prostate or prostatitis can also cause high PSA levels. Discussing PSA test results with a healthcare provider is crucial to understanding what they mean in the context of overall health.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
During a DRE, a doctor inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel the prostate. This examination checks for abnormalities in size, shape, and texture. Although it can be uncomfortable, the DRE is a quick procedure that provides valuable information about prostate health. Often, it is used alongside the PSA test to improve the accuracy of screening.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
Treating prostate cancer depends on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, its aggressiveness, and the patient’s overall health. Treatment plans are often personalized to achieve the best outcomes while minimizing side effects. Here are some common treatment options:
Active Surveillance
For men with low-risk, slow-growing cancer, active surveillance might be recommended. This approach involves regular monitoring through PSA tests, DREs, and possibly biopsies. Treatment begins only if the cancer shows signs of progression. This option helps men avoid or delay the side effects of more aggressive treatments.
Surgery
Surgical options, such as a radical prostatectomy, involve removing the prostate gland and some surrounding tissue. Surgery is often recommended for localized cancer that has not spread beyond the prostate. Advances in surgical techniques, including robotic-assisted surgery, have improved precision, potentially reducing recovery time and side effects.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays or particles to destroy cancer cells. It can be delivered externally (external beam radiation) or internally (brachytherapy), where radioactive seeds are placed directly into the prostate. Radiation therapy is common and can be used alone or with other treatments.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), reduces levels of male hormones, particularly testosterone. This approach can slow the growth of cancer. Hormone therapy is often used for advanced prostate cancer or when cancer returns after initial treatment. It can be administered through injections, oral medications, or surgical removal of the testicles.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill rapidly dividing cancer cells. It is generally used for advanced cancer that has spread to other parts of the body. Chemotherapy can help control the disease, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life, although it may come with significant side effects.
Proton Therapy
Proton therapy is an advanced form of radiation therapy that uses protons instead of X-rays. It delivers more precise doses of radiation to the cancer while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. This targeted approach is especially beneficial for treating prostate cancer, where protecting nearby organs is critical. Proton therapy may offer fewer side effects compared to traditional radiation therapy.
Personalized Care and Support
Managing prostate cancer requires a comprehensive approach that considers not only the physical aspects of the disease but also its emotional and psychological impact. Consulting with healthcare professionals is essential for receiving personalized information and guidance. Each patient’s situation is unique, and treatment plans should reflect individual needs and preferences. Seeking support from loved ones, support groups, and counseling services can help navigate the challenges of living with prostate cancer.
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management play a vital role in maintaining overall health during and after treatment. Staying informed and proactive about your health can make a significant difference in your treatment journey.
Book your appointment now with our expert doctors by visiting our contact page. Early detection and personalized care are key to effectively managing prostate cancer.